Trusted A1 Bed Bug Treatment Houston - Proven Methods
Wiki Article
Recognizing the Lifecycle of Parasites for Targeted Control Strategies
Recognizing the lifecycle of pests is a basic element of effective insect management methods. By comprehending the various phases of development that parasites go through, a more targeted and exact approach can be adopted to regulate their populaces. This knowledge not just drops light on the vulnerabilities within the insect lifecycle but likewise paves the means for executing strategic steps that can interrupt their development and reproduction cycles. Through a much deeper understanding of exactly how bugs flourish and develop, customized control approaches can be developed to address particular factors in their lifecycle, ultimately leading to more effective pest management end results.Relevance of Recognizing Pest Lifecycle
Recognizing the lifecycle of pests is essential for creating efficient and targeted control strategies in insect management. By comprehending the various stages a pest goes through from egg to grownup, bug control specialists can recognize weak spots in the lifecycle where treatment can be most successful. Understanding when larvae are most energetic can aid identify the optimal timing for applying larvicides. Additionally, recognizing the lifespan of a pest species can assist in anticipating population growth patterns and prospective invasion risks.Moreover, acknowledging the particular environmental conditions essential for each and every phase of the bug's lifecycle can guide decisions on environment adjustment or exclusion approaches to reduce and interrupt the lifecycle parasite populaces. This knowledge makes it possible for pest monitoring professionals to implement positive steps instead of counting entirely on responsive treatments, resulting in even more lasting and lasting bug control options. Inevitably, a comprehensive understanding of pest lifecycles equips bug control experts to customize their strategies effectively, decreasing environmental influences and maximizing control results.
Key Phases in Insect Development
To effectively carry out targeted control approaches in parasite management, an important aspect depends on comprehensively recognizing and recognizing the vital phases in bug growth. Bug growth generally consists of numerous vital stages that are essential for their lifecycle and monitoring. The initial stage is the egg phase, where pests lay eggs that later on hatch out into larvae. Larvae then proceed into pupae, a stage where they undergo metamorphosis before arising as adult pests. Understanding these stages is essential as it assists in pinpointing weak spots in the lifecycle where control measures can be most reliable.

Vulnerabilities in Pest Lifecycle
Throughout the various stages of a parasite's lifecycle, distinct vulnerabilities emerge that can be purposefully targeted for effective control procedures. One critical susceptability exists in the egg phase, where pests are usually a lot more vulnerable to specific insecticides or biological control representatives due to their soft external covering, making them much easier targets for intervention. In addition, the nymph or larval stage provides susceptabilities as bugs go through quick development and growth, needing high energy usage that can be made use of by disrupting their food sources or presenting growth preventions. Pupal stages, identified by immobility and transformation, provide a home window for targeted control with physical obstacles or certain therapies that hinder successful emergence. Adult insects, while more durable due to their reproductive capacity, can still be vulnerable during breeding or egg-laying activities, which can be interfered with via pheromone traps or sterilization techniques. Understanding these vulnerabilities in the insect lifecycle is vital for developing specific and reliable control approaches that link efficiently take care of bug populaces while decreasing environmental influence.Implementing Targeted Control Actions
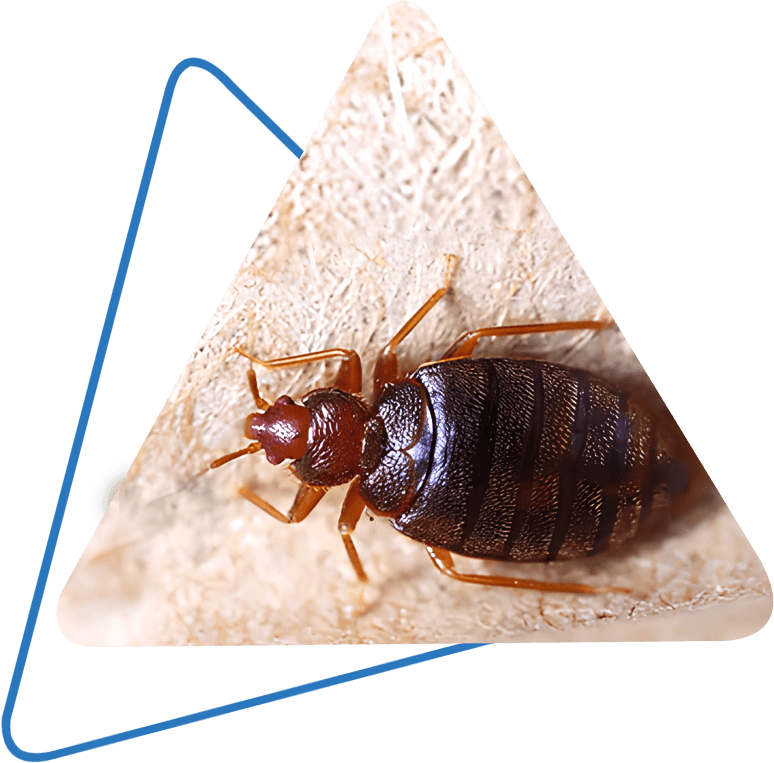
Applying targeted control measures typically includes a multi-faceted approach. This might consist of environment modification to make the setting much less hospitable to pests, such as eliminating standing water for insect control or securing access factors for rodents. In addition, biological control approaches can be utilized, where all-natural killers or pathogens are introduced to maintain bug populations in check.
Chemical control, such as the cautious application of pesticides, is an additional typical technique. However, it is important to make use of these substances judiciously to decrease environmental effect and possible injury to non-target species. Integrated Bug Monitoring (IPM) techniques that combine numerous control steps in a collaborated and lasting fashion are frequently the most efficient in attaining long-term pest management goals. By executing targeted control procedures based on a complete understanding of parasite lifecycles, bug populaces can be successfully managed while reducing risks to human wellness and the environment.
Enhanced Bug Administration Practices

Additionally, the consolidation of organic control representatives, such as natural predators or pathogens of bugs, can aid decrease reliance on chemical pesticides and advertise an extra well balanced ecological community. Executing physical barriers and traps can also be component of boosted pest monitoring methods, using non-toxic and targeted solutions for parasite control. Furthermore, using pheromones and other semiochemicals can interrupt pest breeding patterns and communication, leading to lowered insect populations with time.
Conclusion
In final thought, understanding the lifecycle of linked here bugs is critical for efficient insect administration techniques. By determining essential stages in parasite growth and vulnerabilities in their lifecycle, targeted control measures can be executed to reduce parasite populations. Boosted insect administration practices can help in reducing the dependence on broad-spectrum pesticides and advertise even more eco friendly and lasting bug control approaches. This expertise plays an essential duty in maintaining healthy and balanced communities and farming performance.Recognizing the lifecycle of pests is essential for developing reliable and targeted control methods in parasite administration. By understanding the different phases a parasite goes with from egg to adult, parasite control experts can identify at risk points in the lifecycle where intervention can be most successful. Eventually, a detailed understanding of insect lifecycles empowers insect control experts to customize their methods successfully, minimizing environmental impacts and making best use of control outcomes.
By applying targeted control steps based on a thorough understanding of bug lifecycles, insect populations can be effectively view it now controlled while lessening risks to human health and the setting.
By identifying key phases in parasite growth and vulnerabilities in their lifecycle, targeted control procedures can be executed to decrease bug populations.
Report this wiki page